- Enterprise
- Essentials
The Rise of Cryptocurrency and What It Means for Ecommerce

Choose the Right Ecommerce Platform
Cryptocurrency is a hot topic, both in and outside the financial sphere. No matter what industry you work in, you have probably heard of crypto — even if you don’t know exactly what it is.
So what exactly is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual payment system that is secured by cryptography, which essentially makes it impossible to counterfeit. It is a peer-to-peer ecosystem that enables anyone, anywhere to send or receive money by using digital wallets or exchanges such as Coinbase.
Because crypto exists outside of traditional financial institutions, it is able to bypass banks to verify payments, decentralizing transactions and placing the responsibility in the hands of its users.
Over the last decade, cryptocurrency has exploded in popularity. In 2016, there were 5 million identity-verified cryptoasset users in the world.
That number as of June 2021? 221 million.
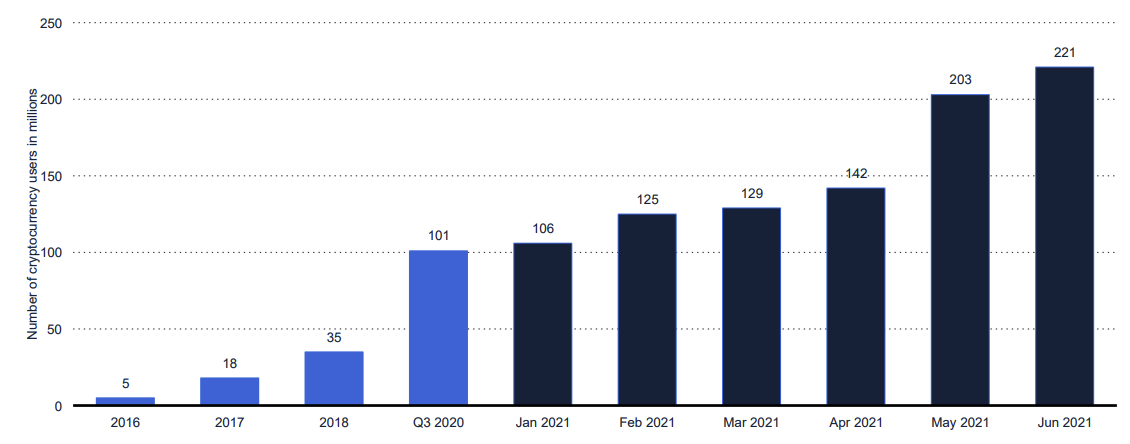
It’s not just individual users, either. Major online retailers such as Microsoft, Home Depot, Whole Foods and Tesla have announced that they are accepting cryptocurrencies within their online stores.
Organizations using ecommerce platforms are not far behind. According to Cryptoslate, the market cap for cryptocurrencies, coins and tokens connected to ecommerce is north of $271 million as of January 2022.
While cryptocurrency is often referred to as the currency of the future, what we’re seeing is that it's also a viable currency for the present.
Discover the Future of Ecommerce
Download our report for an in-depth analysis of consumer shopping trends — from data privacy and sustainability to cryptocurrency and shopping on the Metaverse.
Access NowWhere Did Cryptocurrency Come From?
The first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin, introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto — an unknown identity believed to be a pseudonym — in a 2008 piece titled: “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”
The idea of cryptocurrency came out of a desire for a decentralized form of payment that existed outside of fiat currencies and government-controlled financial institutions.
As Bitcoin’s popularity and legitimacy grew, other companies began to craft their version of cryptocurrency, and as of February 2022, there were around 17,500 unique cryptocurrencies.
How Does Crypto Work?
Cryptocurrencies exist on a digital public ledger called a blockchain, which is a record of all transactions updated and owned by currency holders.
Most units of cryptocurrency — whether Bitcoin, Ethereum or otherwise — are created through a process called cryptocurrency mining. Users generate the currencies, then store and send them using crypto wallets or payment processors like BitPay.
The Blockchain.
A blockchain is a system of recording information that is difficult or impossible to change, hack or cheat. It is at its core a shared, immutable digital ledger of transactions distributed across its entire network. Each block in the chain contains transactions, and each time a new transaction occurs, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger.
Blockchain differs from a typical database in how it stores information — blockchains store data in blocks that are then linked together via cryptography.
There are two primary categories of blockchain: public/permissionless and private/permissioned. With public blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, anybody can participate.
Mining vs Minting.
Cryptocurrency mining is the process of verifying transactions and recording these on digital ledgers — aka, a blockchain. Each time new blocks are mined, the blockchain expands. Cryptocurrency mining serves to both create new coins and maintain a log of all existing transactions.
On the other hand, cryptocurrency minting is the process of validating information, creating a new block and recording that information into the blockchain — thus creating or producing something of tangible value.
Advantages to Accepting Cryptocurrency
A broader market.
Using cryptocurrency as a payment method can grant you entry into an entirely new market comprised of tech-savvy and forward-thinking consumers. A community of these individuals has already been created within the cryptocurrency market, spanning worldwide.
The option to pay through a digital wallet, transaction or credit card platform can allow you to use and view broader markets — all while appealing to consumers around the world.
Lower transaction fees.
Credit card companies and payments apps like Stripe or Square typically charge transaction fees anywhere from 3-5% on each transaction. Many ecommerce sites have built these fees into their online store prices.
Cryptocurrency transactions provide a change of pace, as they typically don’t have transaction fees, and if they do, they are as low as 1%.
Anonymity.
Cryptocurrency payments allow for anonymous purchases by using encrypted wallet addresses. This anonymity allows shoppers to purchase items without giving up their personal information.
Reduce fraud and chargebacks.
The blockchain technology that powers cryptocurrency was built to reduce fraudulent activity.
With cryptocurrency transactions, money is exchanged between hands immediately. It cannot be rescinded, refunded or forged, drastically reducing the chances for fraudulent chargebacks or returns.
Higher security.
It is extremely difficult to reverse a transaction without consent between both parties.
This can provide both retailers and customers with more security when it comes to ecommerce fraud because, without a middle-man such as a bank, there is little to no chance of funds being withdrawn from your account without your explicit permission.
Disadvantages to Accepting Cryptocurrency
Can be volatile.
Cryptocurrency is notoriously volatile. Price volatility is tied directly to a problem of inherent value — it is not backed by any official fiat currency like the US Dollar (USD).
Because of this, crypto is often viewed as akin to gambling. The prices may soar and fall within a week’s span, scaring off potential investors.
Sustainability issues.
Sustainability is a significant issue for cryptocurrency, particularly in an era when climate change is a hot topic. Cryptocurrency mining is known for the significant amount of energy needed in order to mine cryptocoins.
According to CNBC, the energy consumption is so massive that Bitcoin mining consumes even more electricity each year than many countries, including the Netherlands. And this is only one of many thousands of cryptocurrencies.
As carbon and energy taxes become more prevalent, it would not be surprising to see further regulations placed upon cryptocurrency mining — with countries like China already banning the practice.
Less protection for buyers.
With more traditional transactional methods like credit cards, there are built-in protections for the customer regarding fraudulent charges.
These protections do not exist for cryptocurrencies, meaning that the consumer is typically out of luck in the case of fraud. With anonymity being the name of the game in the crypto world, anyone participating in cryptocurrency transactions must be aware of the fact that they are often on their own.
Cryptocurrencies to Be Aware Of
Cryptocurrency is a movement that will only continue to grow in relevance and value. As more and more currencies are being launched weekly, it’s important for consumers and ecommerce businesses to be aware of the top dogs and how they got there.
Bitcoin (BTC).
Bitcoin is the original cryptocurrency that began the whole movement and is still the most commonly traded.
Created in 2009, Bitcoin existed as a minor, mostly unknown form of currency until around 2013, when it began to be seen as a viable form of payment processing. Bitcoin has surged in recent years, raising its legitimacy and providing an example for other forms of cryptocurrency.
Ethereum (ETH).
Ethereum was developed in 2015 as a blockchain platform with its own cryptocurrency and is currently the second most popular cryptocurrency available.
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum’s presence as both a platform and currency allows it to live as a place for developers to create additional decentralized applications without strict codes or contracts — contributing to the open vision of Bitcoin while existing as its own thing.
Cardano (ADA).
Cardano is the cryptocurrency platform, while ada is the name of the currency itself. Began by a co-founder of Ethereum, Cardano prides itself as a cryptocurrency created with a research-based approach and is led by a team of engineers, mathematicians and cryptography experts.
With Cardano, each individual who owns ada currency also holds a stake in the Cardano network itself.
Binance Coin (BNB).
Binance coin is a cryptocurrency that operates as a payment method for trading on the Binance Exchange, one of the largest crypto exchanges in the world.
Initially created as a way to pay for discounted trades on the exchange platform and operating on the Ethereum blockchain, Binance Coin is now its own entity and can now be used for payments elsewhere.
XRP.
Formerly named Ripple, XRP is the cryptocurrency used by RippleNet, a blockchain-based payments network.
XRP was designed to facilitate faster, cheap cross-border transactions between financial institutions. Instead of waiting days for a transaction to complete, with XRP, this process can be completed in minutes or even seconds — at a fraction of the transaction costs.
Litecoin.
Litecoin was one of the first cryptocurrencies, launching in 2011 in the footsteps of Bitcoin as the “lite” version of its predecessor.
Unlike Bitcoin, Litecoin is able to produce its coins at scale. While Bitcoin can never exceed 21 million coins, Litecoin can accommodate 84 million. Though this gives it a greater supply, it does limit its market cap.
Dogecoin.
Originally created in 2013 as a joke or “meme coin,” Dogecoin is no longer a laughing matter as the price of the cryptocurrency soared in 2021 past many, more serious alternatives.
Dogecoin, which uses its eponymous image of a Shiba Inu, is now used as an accepted form of payment by several major companies, including those owned by the billionaires Mark Cuban and Elon Musk.
The NFT and Cryptocurrency Way
As cryptocurrency continues to grow in popularity and more companies accept it as a valid form of payment, it is no surprise that other forms of digital assets have begun to pop up.
Among these assets is the non-fungible token, better known as an NFT.
What are NFTs?
NFTs are a non-interchangeable unit of data stored on a blockchain. A non-fungible token means that the token itself is unique, unable to be replaced with something else.
An example would be a piece of digital art. Unlike standard cryptocurrencies, which can be replaced for other cryptocurrencies, an NFT stands alone. It can be exchanged for different, unique NFTs, but they ultimately remain the same thing.
The surging popularity of NFTs is no less than staggering. As a study by Statista shows, the market capitalization of transactions involving an NFT grew from $50 million in 2018 to almost $340 million in 2020 — a nearly 700% increase.
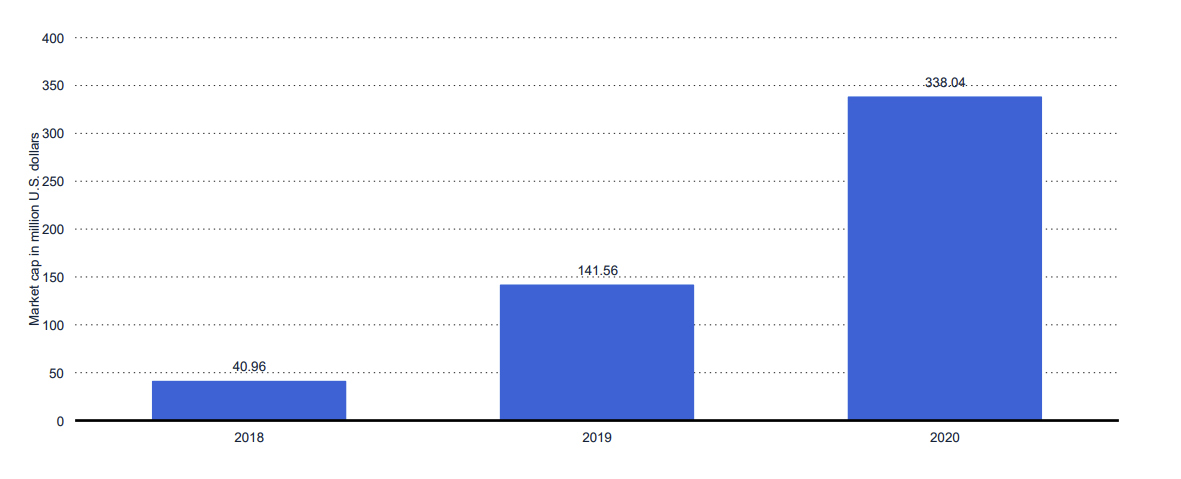
Large corporations like Walmart have already started planning on launching their own cryptocurrencies and NFTs. For companies wanting to stay competitive in the shifting financial landscape, it is important to understand what NFTs are because it may not be too long before they’re embedded in every market.
The Final Word
There are concerns with cryptocurrency, and it remains to be seen if it will ever reach the level of viability and sustainability that has defined fiat currencies around the world.
However, for companies looking to the future, cryptocurrency presents a way to remain relevant and maintain the cutting edge as the world of finance continues to shift to digital currency.
Within the realm of ecommerce, it may not be long before cryptocurrencies begin to replace traditional ways of online transacting such as credit cards or financial platforms.
Even if crypto never reaches that level, having another alternative payment option can only broaden your potential market and expand your potential customer base.
FAQs About Ecommerce Cryptocurrency
What is blockchain and cryptocurrency, are they the same?
They are not the same thing.
As described above, blockchains are the digital ledger that deposits and records crypto transactions, while cryptocurrency is the actual currency used.
To put it plainly, blockchains are the database; cryptocurrency is the money.
How are cryptocurrency transactions recorded?
Cryptocurrency transactions are recorded using blockchain technology.
For example, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are based on a blockchain, which again acts as a public ledger. Every transaction performed is recorded within the blockchain — all while keeping each user’s identity and balance secure and anonymous.
What is a cryptocurrency wallet?
A crypto wallet is a program or physical device that allows you to store your keys safely and securely. They also enable the sending and receiving of crypto transactions, as well as transfers between bank accounts.
Crypto wallets typically consist of two kinds of keys, private and public. Private keys hold the passwords that grant you access to your cryptocurrencies, while public keys serve as the address to send crypto to your wallet.
Why are we seeing more adoption in ecommerce?
Cryptocurrencies are growing in popularity within ecommerce for two simple reasons.
The first being that they both exist within the digital sphere, and make natural companions. An ecommerce platform is designed for use online and adding crypto capabilities makes sense for an online consumer base.
Secondly, and most succinctly, cryptocurrency presents another form of payment. Why should your ecommerce store — or anyone for that matter — fight against alternative digital payments options? It can only add to your customer base and broaden your market.
What are the use cases in ecommerce?
Without most people knowing it, blockchains are already currently used by retailers and ecommerce merchants today.
The most common usages of blockchains occurring include loyalty programs, supply chain management, logistics, and tracking products and service. Through the use of automation, these blockchains have already helped to expedite these services and save organizations money.